![]()
![]()
Networking service systems and related standards
|
3.4 T.120 Data |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The T.120 is a recommendation of ITU, which contains a series of communication and application protocols and services supporting real-time, multipoint data communications. [25] T.120 specifies the document conferencing and application sharing (or data conferencing) section of a multimedia teleconference. It describes a method to distribute files and graphical information in real-time efficiently and reliably during a multipoint multimedia meeting. These standards are proposed to assure interoperability between each end user, to specify infrastructure protocols for audiographic or audiovisual applications and to permit data sharing among participants in a multimedia teleconference, which includes white board image sharing, graphic display information, image exchange and application sharing. It covers the audiographic portion of the H.320, H.323, and H.324 series and operates either within these or by itself.[26] Architecture: There are three main layers that are needed to deliver the best quality that can be provided by T.120. [31]
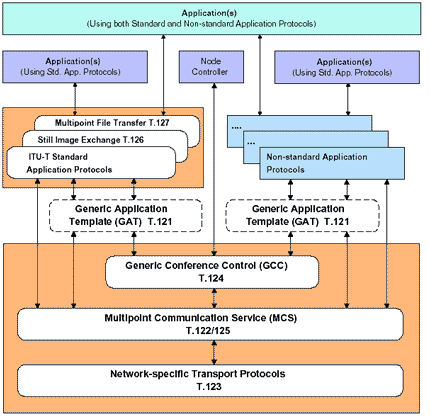
T.120 is based on a multilayered structure where the defined protocols and service definitions are supplied between layers. As shown in Figure A-2, T.122, T.123, T.124, and T.125 are located on the lower level layers which specify a mechanism to enable multipoint data communication between applications. T.126 and T.127 are located on the upper level layers to support conferencing applications, such as shared whiteboarding and multipoint file transfer. Using these protocols applications can share the same conference with other applications that use other protocols. [25] Figure A-2 The T.120 architecture. [25] Most of the recommendations in T.120 are summarized in Table A-1. [26] Table A-1 ITU T.120 Standard[26]
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Designed by Yong Qiu Liu.
Copyright © 2006 All rights reserved